🔎Hello again,
A lot has been going on, so I missed out on posting yesterday. So without any delay let me tell you a few more points about the TCA cycle; that I raised in our previous post in the form of questions.
Q1. why the TCA cycle is called the final common oxidative pathway?
Ans: The TCA cycle is considered the final common oxidative pathway for all the foodstuffs because all the major ingredients of foodstuffs are finally oxidized through the cycle. Almost all the biochemical processes use ATP for meeting energy needs- like muscle contraction active transport biosynthetic reactions, etc. All the metabolic Pathways converge into this pathway as follows:
Integration of major metabolic Pathways:
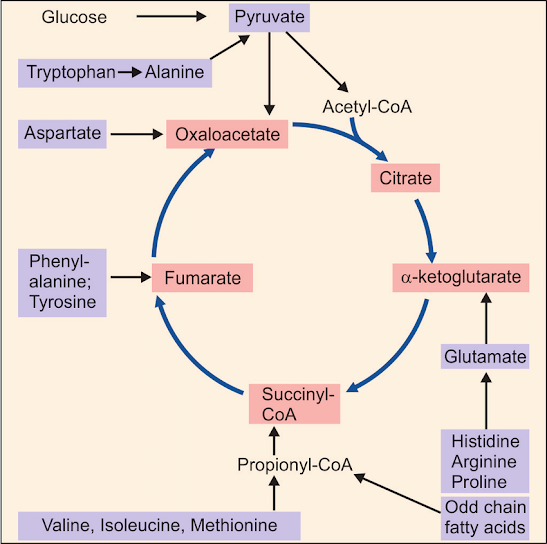
- Carbohydrates are metabolized through glycol lighting pathway to pyruvate then converted to acetyl CoA a which enters the citric acid cycle.
- Fatty acids through beta-oxidation are broken down to acetyl CoA and then enter this TCA cycle
- Glucogenic amino acids after transamination and at some or other points in this cycle. Ketogenic amino acids are converted into acetyl CoA.
- The integration of metabolism is achieved at the junction point by key metabolites. Several Pathways can converge at this point with the result that carbon atoms from one source can be used for the synthesis of another. Important intermediates are pyruvate acetyl CoA and oxaloacetate.
Ans: the main significance of the TCA cycle are :
- complete oxidation of acetyl CoA.
- 1. ATP generation
- 2. the final common oxidative pathway
- 3. integration of major metabolic Pathways
- 4. fat is burned on the wick of carbohydrates
- 5. excess carbohydrates are converted as neutral fats
- 6. no net synthesis of Carbohydrates from fats
- 7. carbon skeletons of amino acids finally enter the citric acid cycle
- 8. amphibolic pathway
- 9. anaplerotic role.
Q3.What are the functions of the TCA cycle?
Ans: The TCA cycle has the following functions:
- The final common oxidative pathway that oxidizes acetyl CoA to carbon dioxide
- .The source of reduced coenzymes that provide the substrate for the respiratory chain
- The link between catabolic and anabolic pathways (Amphibolic role).
- Precursors for the synthesis of amino acids and nucleotides.
- Components of the cycle have direct or indirect controlling effects on key enzymes of other pathways.
a) oxaloacetate is the precursor of aspartateb) alpha-ketoglutarate it can be made into glutamatec)Succinyl CoA a is used for the synthesis of hemed)mitochondrial citrate is transported to the cytoplasm where it is cleaved into acetyl CoA, which then is the starting point of fatty acid synthesis.
- 1. pyruvate to oxaloacetate by pyruvate carboxylase enzyme
- 2. glutamate is transanimated to Alpha-ketoglutarate and aspartate to Acetate. 3. Other important amino acids entering the TCA cycle are shown in figure 1.
- 4. pyruvate can be carboxylated to malate by NADP+ dependant malic enzyme.
Have a great day!



0 Comments